Project management is a rapidly evolving field, with new techniques, tools, and best practices emerging all the time. To stay ahead of the curve, project managers and organizations must constantly adapt and improve their project management processes.
The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) has long been a key resource for professionals seeking to improve their project management skills and knowledge. The recently released PMBOK 7th edition represents a significant update to the framework, incorporating new insights and best practices that reflect the changing landscape of project management.
If you have been planning to take your PMP certification exam, then you must have wondered what the difference between the PMBOK Guide 6th edition and the 7th edition is.
In this article, we’ll explore what PMBOK is in project management, why PMBOK is changing, the differences between PMBOK’s 6th & 7th editions, and more. Are you ready? Let’s dive in!
What you'll find in this article
- 1 What is PMBOK in project management?
- 2 Why is PMBOK changing?
- 3 PMBOK 7th edition
- 4 Seven differences between PMBOK Guide 6th and 7th edition
- 5 Visual for changes from the PMBOK 6th edition to the PMBOK 7th edition
- 6 PMBOK guide and the PMP® certification exam
- 7 How APEX Global can help you with PMP exam preparation
- 8 Wrapping up
What is PMBOK in project management?
Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) is the full set of processes, terminologies, best practices, and guidelines that are accepted as standard within the project management industry. Explore the top 50 project management terms you need to know here.
The PMBOK guide is published by the Project Management Institute (PMI) to provide a global standard for all things project management. According to PMI, a PMBOK Guide is PMI’s flagship publication and is a fundamental resource for effective project management in any industry.
PMBOK helps companies standardize processes across departments, tailor processes to meet specific needs, and prevent project failures.
Why is PMBOK changing?
PMI released the first edition of the PMBOK guide in 1996, and since then, it has been releasing a new version after every four years. The latest version of the guide is the 7th edition, which was published in August 2021, and the previous version – the PMBOK 6th edition, was published in 2017.
The PMBOK guide is changing in part due to the industry’s shifting needs and demands. As the industry evolves, project management techniques evolve, and the guide needs to keep up with these changes.
Another reason why it is changing is to provide a more holistic approach to project management.
PMI learned through feedback on PMBOK 6th edition that, although it’s a well-acclaimed project management reference, the guide was considered dry, difficult to understand and to put into practice.
The latest version – PMBOK 7th edition, includes a focus on stakeholder management, project leadership, and strategic & business management.
This makes it possible for project managers to cope with digital transformation with a more comprehensive approach to managing projects, which may lead to improved project outcomes. These changes are necessary for the guide to remain relevant and useful in the industry.
PMBOK 7th edition

The PMBOK 7th edition book contains two distinct parts:
I. The Standard for Project Management
PMI states that this is the document that carries the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) designation.
II. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge
This guide provides a framework for applying the standard.
According to PMI, the 7th edition of the PMBOK® Guide:
- Reflects the full range of development approaches (predictive, traditional, adaptive, agile, hybrid, etc.)
- Provides an entire section devoted to tailoring the development approach and processes
- Expands the list of tools and techniques in a new section, “Models, Methods, and Artifacts”
- Focuses on project outcomes in addition to deliverables
- Integrates with PMIstandards+™ for access to content that helps the user apply the PMBOK® Guide on the job
Seven differences between PMBOK Guide 6th and 7th edition
There are many significant differences between PMBOK 6th edition and PMBOK 7th edition.
At the most basic level, one huge difference between them is the sheer size of the physical book; the new edition comes in just 370 pages as compared to the earlier version, which consisted of 756 pages.
Let’s see the other major differences between PMBOK 7 and PMBOK 6 in detail.
1) Process-based to principle-based
In PMBOK 6th edition, the standard for project management primarily focuses on processes, which are organized into 5 Process Groups:
A. Initiating
B. Planning
C. Executing
D. Monitoring & Controlling
E. Closing
Now in the PMBOK 7th edition, the focus has shifted to 12 Project Delivery Principles. These principles specify the “what” and “why” of the project delivery. They describe a fundamental truth, norm, or value and are not prescriptive
The following are the 12 Project Delivery Principles:
- Be A Diligent, Respectful, and Caring Steward
- Create A Collaborative Project Team Environment
- Effectively Engage With Stakeholders
- Focus On Value
- Recognize, Evaluate, And Respond To System Interactions
- Demonstrate Leadership Behaviors
- Tailor Based On Context
- Build Quality Into Processes And Deliverables
- Navigate Complexity
- Optimize Risk Responses
- Embrace Adaptability And Resiliency
- Enable Change To Achieve The Envisioned Future State
These principles shape how you think about project management and give you guardrails for behavior while letting you lead the project any way you see fit within those parameters.
2) Knowledge Areas to Project Performance Domains
The 10 Knowledge Areas of PMBOK 6 have been replaced by a group of 8 Performance Domains in PMBOK 7. The PMI defines a domain as “groups of related activities that are critical for the effective delivery of project outcomes.”
The 8 Performance Domains are:
- Stakeholders
- Team
- Development Approach and Life Cycle
- Planning
- Project Work
- Delivery
- Measurement
- Uncertainty
These domains are designed to provide a comprehensive view of the various elements that contribute to a project’s success.
3) Value delivery system
The value delivery system is a new concept introduced in the standards section of PMBOK 7 along with project delivery principles.
This section includes the following:
- Creating Value
- Organizational Governance System
- Functions Associated with Projects
- The Project Environment
- Product Management Considerations.
The PMBOK 7th edition, in contrast to the PMBOK 6th edition, emphasizes more on the project team’s capacity to provide value-based results as opposed to the technical processes, inputs, tools, techniques, and outputs of the project manager.
Projects are considered as systems to deliver value. The perspective is changed from the governance of portfolios, programs, and projects to the value chain and value delivery. It emphasizes that projects don’t just produce outputs but enable those outputs to drive results that ultimately provide value to the organization.
4) A focus on agile methodologies
The PMBOK guide has traditionally focused on the Waterfall methodology, which is a linear, sequential approach to project management. However, in recent years, Agile methodologies have gained popularity due to their flexibility and adaptability to changing project requirements.
Thus the PMBOK 7th edition includes more comprehensive guidance on Agile methodologies than the 6th edition. The new Agile Project Management Knowledge Area and the Tailoring and Adaptability section provide more detailed guidance on how to apply Agile practices within the project management framework, along with more examples and case studies of Agile project management practices.
The 7th edition also introduces the concept of hybrid approaches, which combine traditional and agile methodologies to meet the unique needs of each project. It recognizes that not all projects require strict adherence to traditional project management processes and that hybrid approaches can be more effective in some situations.
5) Tailoring
One of the most significant changes introduced in the PMBOK 7th edition is a new emphasis on tailoring project management processes to better suit the needs of individual projects.
This change reflects a growing recognition that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to project management and that each project is unique and requires a tailored approach.
Tailoring project management processes involves adapting the PMBOK framework to fit the specific needs and characteristics of a project. The PMBOK 7th edition provides a set of guiding principles that can be used to tailor project management processes, including the project’s size, complexity, and risk level, as well as the industry, culture, and geographic location in which the project is being carried out.
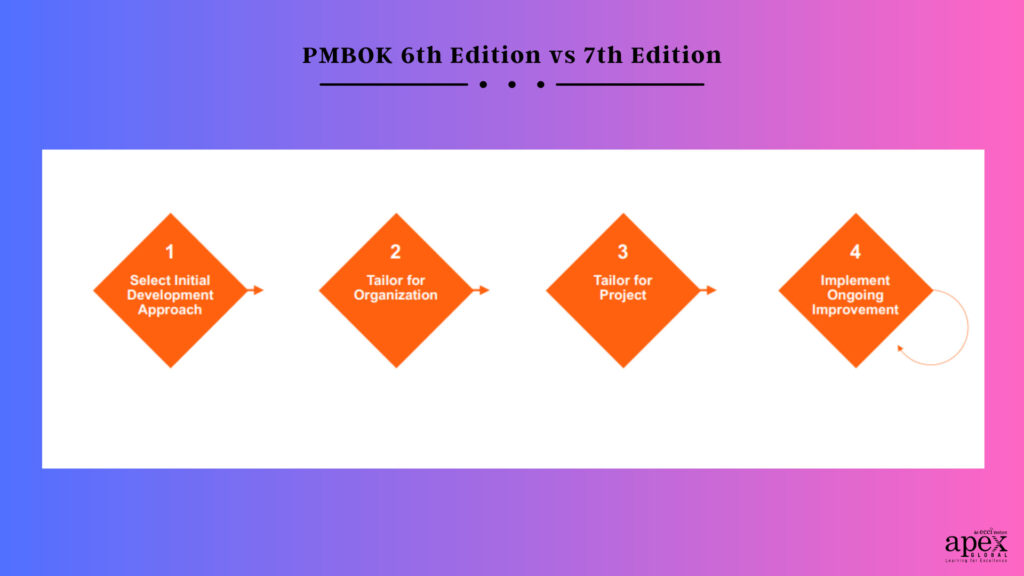
Thus the PMBOK 7th edition recognizes that project management is not a static process but rather a dynamic one that requires ongoing adjustments and modifications to suit the changing needs of a project. This shift towards a more flexible and adaptable approach to project management reflects the growing importance of Agile methodology, which emphasizes adaptability and continuous improvement.
6) Models, Methods, and Artifacts
One of the improvements introduced by the PMI in the PMBOK 7th edition is Models, Methods, and Artifacts. In simple terms, this is a set of tools to help you perform the project management job successfully. PMI defines them as ‘options for enabling outcome’.

In particular, PMBOK 7th edition defines each of them in the following way:
a. Model
A model describes a thinking strategy to explain a process, framework, or phenomenon. Sample models include Process Groups, ADKAR, Situational Leadership, etc.
b. Method
A method is the means for achieving an outcome, result, or project deliverable. Sample methods include Probability and Impact Matrix, Lessons Learned, Project Closeout, etc.
c. Artifact
An artifact is a template, document, output, or project deliverable. Sample artifacts include Project Charter, Risk Register, Stakeholder Engagement Plan, etc.
7) Other notable differences between the two editions
(i) Expansion of the PMI Talent Triangle
Another notable change in the PMBOK Guide 7th edition is the expansion of the PMI Talent Triangle. The Talent Triangle is a framework that defines the three skill areas required for project management success: technical project management, leadership, and strategic and business management. The 7th edition has expanded this framework to include a fourth area, which is digital transformation.
(ii) Changes in terminology and definitions
In addition to changes in methodology and project management processes, the PMBOK 7th edition also brings about important changes in terminology and definitions. The aim is to provide a more consistent and universal language that can be easily understood by all stakeholders in the project management field.
One of the changes is the replacement of the term “project documents” with “project records”. Another change is the replacement of the term “project management plan” with “project management performance baseline”.
The PMBOK 7th edition also introduces new terms such as “Agile manifesto”, “Agile team”, and “Product Owner”. The introduction of these new terms and definitions highlights the importance of understanding Agile methodology and its application in project management.
Furthermore, the PMBOK 7th edition also redefines the concept of “stakeholders” in project management. The definition now includes anyone who may be affected by the project or its outcomes, including individuals or groups who may not have a direct role in the project.
Visual for changes from the PMBOK 6th edition to the PMBOK 7th edition
PMI has shared the following infographic on its website regarding the changes from PMBOK 6th to 7th edition.

PMBOK guide and the PMP® certification exam
PMP® (Project Management Professional) is the most recognized project management certification around the world, with nearly 1 million PMP-certified individuals.
The PMBOK guide is listed as one of the references for preparing for the PMP® exam, but according to PMI, it is not a test preparation tool. As stated in its FAQ, the PMP® exam is based on the Exam Content Outline (ECO) and not on the PMBOK Guide. The ECO contains the summary of the research conducted to create the PMP® exam and includes the most critical tasks required for project managers to master in their roles.
Although the latest PMBOK edition takes a radically different approach to describing the Body of Knowledge, it does not invalidate or replace the technical knowledge previously published in the PMBOK 6th edition.
Therefore, if you’re planning to take the PMP® certification exam, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with both PMBOK’s 6th and 7th editions. Doing so will help ensure that you have a comprehensive understanding of the critical concepts, best practices, and guidelines for effective project management required to pass the exam. Check out our list of 10 project management best practices for successful project management here.
How APEX Global can help you with PMP exam preparation
If you are preparing for the PMP® exam, you will need expert guidance on making the connections between the material in PMBOK 6th edition and PMBOK 7th edition and the PMP® exam content outline.
If you are looking for structured training to pass your PMP® certification, we recommend APEX Global’s Project Management Professional ® Course.
Our PMP training is conducted by accredited instructors who will help you master a comprehensively structured curriculum supplemented with industry-relevant examples. You’ll get access to PMI-authorized PMP course contents, and our training will help ensure that you pass the PMP® exam on your first attempt and help your organization achieve strategic initiatives.
So, enroll in APEX Global’s PMP training course today and take the first step towards achieving your Project Management Professional certification!
Wrapping up
The PMBOK 7th edition has introduced a new era for the PMBOK guide and project management standard. The differences between PMBOK’s 6th and 7th editions reflect the changing landscape of project management.
While there are several differences between the two editions, it’s important to remember that the PMBOK Guide 7th edition builds on the foundation established by the previous editions. The changes in the 7th edition are aimed at improving project management practices and ensuring project success in today’s fast-changing business environment.
Whether you’re a seasoned project management professional or just starting your career in project management, it’s essential to stay up to date with the latest developments in the field. The PMBOK Guide 7th edition is an invaluable resource that can help you navigate the challenges and complexities of modern project management.
By embracing the changes outlined in the new edition, project management professionals can position themselves for success in the years ahead.
If you’re looking to expand your project management knowledge further, here’s a list of 8 highly recommended books that will help you become a better project manager.


