Imagine a world where factories run themselves, customized products are created on demand, and machines communicate with each other seamlessly. A world where Artificial Intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) converge to create a new era of manufacturing and business.
This is the world of Industry 4.0, where the boundaries between the physical and digital worlds are blurring, and innovation knows no limits.
The term Industry 4.0 might sound like the name of a video game or a sci-fi movie to those who are new to the manufacturing sector. However, it actually refers to the fourth Industrial Revolution, the biggest shift to hit global manufacturing since automation.
So what does the fourth Industrial Revolution actually mean?
In this blog, we’ll talk about what Industry 4.0 is, the technologies driving it, the benefits and challenges it brings, and two real-world examples of Industry 4.0 technologies.
Ready to explore the exciting world of Industry 4.0? Let’s go!
What you'll find in this article [hide]
- 1 From steam engines to computers: Historical context for Industry 4.0
- 2 What is Industry 4.0?
- 3 Nine technologies driving Industry 4.0
- 4 Seven benefits of Industry 4.0
- 5 Two challenges in the implementation of Industry 4.0
- 6 Two real-world examples of Industry 4.0: Digital manufacturing in action
- 7 Riding the wave of digital manufacturing
From steam engines to computers: Historical context for Industry 4.0
Calling something a revolution is a huge claim. The truth is that many “revolutions” we’ve heard about have not lived up to the hype.
Then, what makes Industry 4.0 a true revolution?
It is the capacity of Industry 4.0 technologies to disrupt existing orders. Technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence, etc., all have the potential to undermine and massively transform core institutions.
To put this into context, let’s take a brief look at the previous three industrial revolutions.
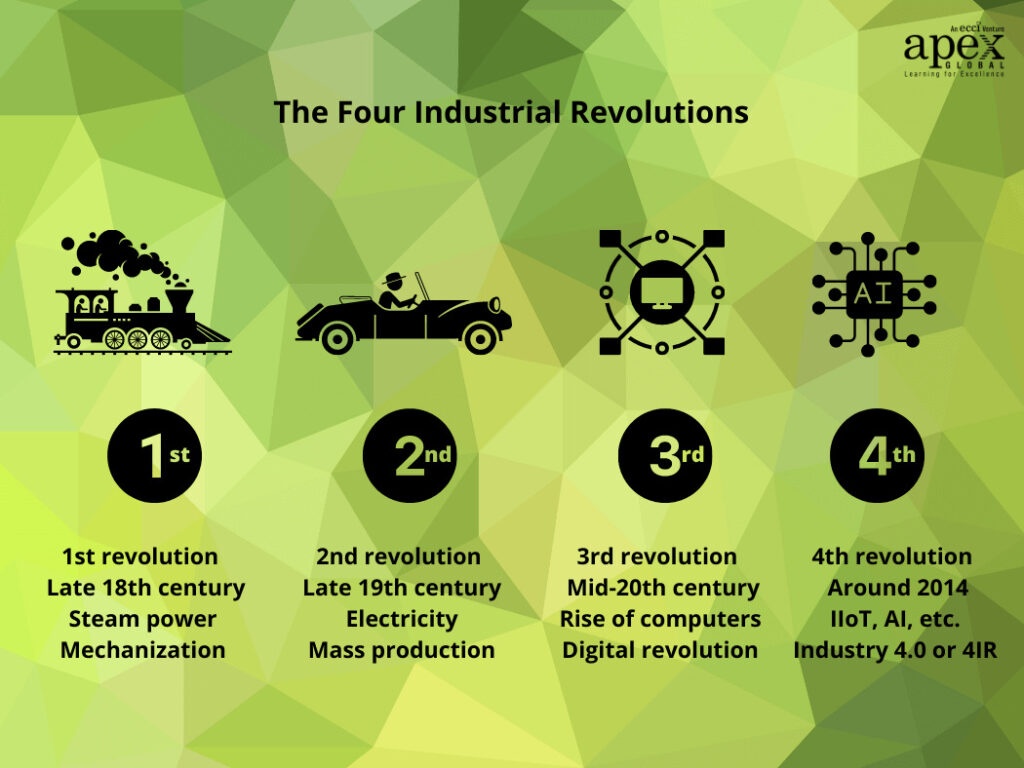
i) First Industrial Revolution – Mechanization
During the late 18th century in Britain, the first industrial revolution ushered in a new era of mechanization, replacing human and animal power with water and steam power. This revolution transformed society with the advent of trains, mechanized manufacturing, and lots of smog.
ii) Second Industrial Revolution – Mass production
A century later, the second industrial revolution brought technology to industries that resulted in new forms of energy, including oil, gas, and electricity. The introduction of these new power sources, along with more advanced telephone and telegraph communications, brought mass production to manufacturing processes.
iii) Third Industrial Revolution – The digital revolution
The third industrial revolution, which began in the mid-20th century, gave rise to computers and telecommunications. This revolution also opened the door for new technologies that allowed for advancements in biotechnology and space exploration.
These three were all called ‘revolutions’ because the innovation behind them didn’t just slightly improve productivity and efficiency, it completely revolutionized how products were created and how jobs were performed.
Now, sometime in the last decade, manufacturing entered a period of transformation. New industrial technologies started quickly emerging, like cloud computing, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, big data analytics, 3D printing, cyber-physical systems, etc.
Together, these technologies inaugurated a Fourth Industrial Revolution. This revolution, also called Industry 4.0, is changing manufacturing at a pace and scale similar to the invention of steam power or electricity. Let’s explore this revolution in more detail in the next section.
What is Industry 4.0?
Augmented reality, machine automation, additive manufacturing, and more.
Industry 4.0, the Fourth Industrial Revolution, and 4IR all refer to the current era of automation, monitoring, and analysis of supply chains through smart technology.
This revolution marries manufacturing operations with the Internet of Things to create systems that are not only interconnected but communicate, analyze, and use data to make important decisions related to manufacturing.
It is run by intelligent, autonomous systems that monitor and manage physical objects like machinery, robots, and vehicles using computer-based algorithms.
Everything in your supply chain becomes ‘smart’ thanks to Industry 4.0, including your factories, warehouses, and logistics centers.
But it doesn’t stop at the supply chain. It interconnects with enterprise resource planning (ERP) and other back-end systems to provide companies with a level of visibility and control never possible before. Industry 4.0 is ultimately a major part of any company’s digital transformation.
Fundamentally, Industry 4.0 is not only about investing in new technology and equipment to improve manufacturing efficiency, it’s about reimagining the way your entire company functions and grows.
Nine technologies driving Industry 4.0
The concept of Industry 4.0 is not simple. It encompasses various technologies and is applied in a wide range of situations.
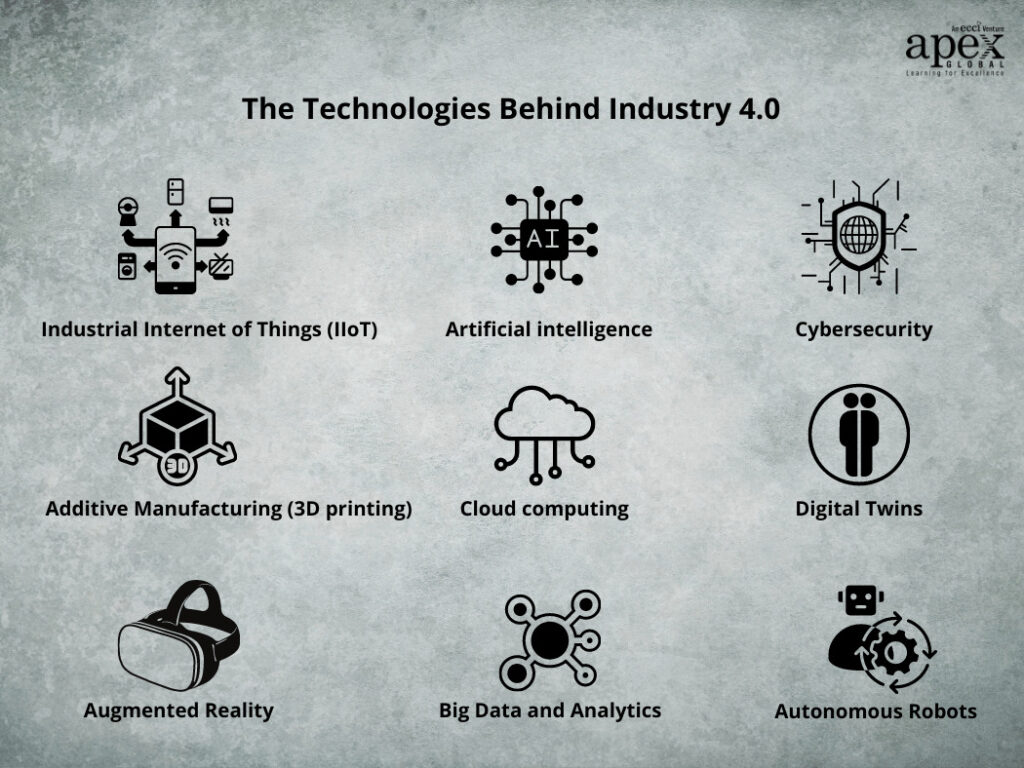
There are 9 technologies that define Industry 4.0 at its core. Each one is similar in nature but, when integrated together, creates a capability that has never before been possible.
These 9 technologies are:
- Cloud computing
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
- Big data and analytics
- Artificial intelligence
- Cybersecurity
- Digital twins
- Augmented reality
- Autonomous robots
- Additive manufacturing (3D printing)
We may have no idea what the future of Industry 4.0 holds, but all of the above components are essential for businesses to stay competitive as they strive to build the perfect smart factory.
Seven benefits of Industry 4.0
Now that you learned what Industry 4.0 is and the technologies that are driving it, you must be wondering what Industry 4.0 has to offer you. And that’s exactly what we’re going to discuss in this section.
The 7 key benefits of Industry 4.0 technologies are:
a. Enhanced productivity
They enable manufacturers to significantly improve their production output by putting in less effort. They make it possible to employ all of the available resources efficiently and affordably at the same time.

b. Optimised supply chain management & security
They enable you to have greater supply chain visibility so that you can identify bottlenecks and other issues before they affect the output of your production lines.
c. Optimized manufacturing process
Greater collaboration along the whole supply chain is made possible by improved analytics, shared data, and connectivity, which may ultimately boost manufacturing industry innovation, efficiency, and productivity.
d. Convenience
They’ll enable the business owners to decentralize the workload and allow the employees to do more domain-specific tasks. The system’s interconnectedness also makes it possible for you to monitor the company remotely from your home and share data with colleagues for analysis easily.
e. Reduced costs
Becoming a Smart Factory does not happen overnight, and it won’t happen on its own. To achieve it, investing is required, so there are upfront costs. However, thanks to Industry 4.0 technology, the cost of manufacturing will be lower at your facilities.
f. Deepen customer relationships
They allow businesses to produce digital goods and services, better meet delivery deadlines, make customized goods more quickly, and offer better customer support, all of which help you in deepening customer relationships.
g. Empowered people
They enable your people to have access to better data so that they can have enhanced oversight as well as the ability to make data-driven decisions. With automation technologies & advanced workflows, you can also eliminate the need for your people to work on repetitive tasks. Learn more about automation in our article about BPA here.
Two challenges in the implementation of Industry 4.0
As you consider whether or not to invest in Industry 4.0, you may also be thinking about some of the potential challenges associated with incorporating new technology and processes into your organization.
You’ll be glad to know that there are almost no drawbacks to the interconnected system apart from these two:
- Data & IT security: Your data’s security may be compromised, especially if you use cloud storage or any other online repository. Designs and prototypes could be stolen if there are no security protocols in place. To help combat this issue, companies need to anticipate any vulnerabilities and develop strategies to prevent attacks or deal with them efficiently. Read more about how to plan for your disaster recovery here.
To ensure the security of your organization’s data in the Industry 4.0 era, consider enrolling in our ISMS Practitioner course for comprehensive training in information security management.
- A gap in technical skills: The technology may be too advanced for you to fully understand, and technical aspects may also be overlooked. Fortunately, most software includes detailed technical support manuals and hotlines to help with technical concerns. You can also turn to online courses, which can teach your employees how to use a program that usually takes only a few days to complete.
Two real-world examples of Industry 4.0: Digital manufacturing in action
Enough with the advantages and challenges. At this point, you must be curious to know if any real companies around the world have successfully implemented Industry 4.0 technologies. Well, we are glad to tell you that not only companies have implemented them successfully they are being benefitted from them every day.
Let’s spotlight a couple of real-world examples to show you that Industry 4.0 is already a reality.
A. Bosch Software: When data analytics meets manufacturing
Bosch Automotive Diesel Systems Co is a consumer goods company located in Wuxi, China. It is one of the most important bases of the Bosch Group. This company has combined IIoT and Big Data in order to drive the digital transformation of its factory in China.
And how exactly is it doing it? It has connected its machines to monitor the overall production process at the core of its factory.
- Sensors are embedded into the machines in the factory that are used to gather information about their cycle times and conditions.
- Modern data analytics tools analyze this data in real-time and notify the working staff when any production bottlenecks are found.
Thus, it can now easily predict equipment failures, enabling the factory to schedule maintenance operations well before any failures occur. As a result, the factory is able to keep its machinery working for extended periods of time.
The company states that using data analysis in this way has contributed to more than 10% output increase in certain areas whilst improving delivery and customer satisfaction.
Ultimately, having more knowledge about the plant’s operations helps the entire organization make decisions that are better and faster, which enables it to minimize equipment downtime and optimize production procedures.
B. Team Penske: Racing to win with digital twins
Team Penske, an American pro racing team, wanted to speed up the race car development process. It partnered with Siemens in 2018, gaining access to advanced digital design and simulation solutions – including digital twins.
This gave Team Penske engineers a virtual testing ground for developing new components and enhancing vehicle performance before they ever touched the actual vehicle.
- A race car digital twin was built by fitting sensors onto a real car.
- These sensors gather information on the engine control, tire pressure, and wind speed, which is then used to create a virtual car model.
- This model enabled engineers to evaluate different design configurations and make efficient, data-driven design changes at a very rapid pace.
This ultimately helped Team Penske to carry out a cheaper, more resource-efficient product testing process. As a result, it completed the best racing season in the team’s history, was able to deliver parts to the track in less time, and achieved the 200th IndyCar and 500th team wins.
Both of these examples illustrate how organizations are integrating the latest technologies to enhance the performance of their operations. Hopefully, now you are able to get an idea of how much the world will change with the implementation of these awesome technologies.
Riding the wave of digital manufacturing
Industry 4.0 is poised to revolutionize the manufacturing industry and beyond. By harnessing the power of digital technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain, businesses can unlock new opportunities, streamline operations, and enhance their bottom line.
While there are certainly challenges to be faced in this new era, the benefits are undeniable. Companies that embrace the potential of Industry 4.0 will be well-positioned to succeed in a rapidly evolving marketplace.

So, whether you’re just getting started or already well on your way, the time is now to join the revolution and embrace the future of manufacturing and business.
Are you ready to drive innovation and new business models in your own organization? Enroll in APEX Global’s Business Innovation through Industry 4.0 course today and learn everything you need to know about Industry 4.0.
Have any questions? Reach out to us today at training@apexgloballearning.com. We’d love to hear from you!


