Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that relies on a collaborative team effort, which aims to achieve business success by systematically reducing waste and improving operational processes. It is comprised of two concepts namely Six Sigma and the Lean Method. The former focuses on reducing defects, while the latter puts emphasis on waste elimination.
What you'll find in this article
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a flexible system driven by a good grasp of customer insight and a rigorous application of facts and statistical analysis, with a goal of introducing process improvements to businesses. It is based on the concept of process variation,” wherein statistical tools and data are used to reduce waste and inefficiencies.
Six Sigma DMAIC Framework
Projects that follow the Six Sigma methodology use the Five DMAIC phases, which stands for:
Define, which is used to identify the problem such as who the customers are, their requirements, expectations, and boundaries.
Measure, which is used to quantify the problem. It includes measuring the performance of the core business process, developing a data collection plan for the process, collecting data from various sources to help determine metrics, and comparing customer survey results to determine issues or areas for improvement.
Analyze, which is used to identify the cause of the problem. This is used to identify gaps between current conditions and the performance goal, prioritize opportunities for improvement, and identify sources of variation.
Improve is used to implement and verify the solution. This is where you create innovative solutions, develop a plan, and deploy it for implementation.
Control, which stands for maintenance of the solution, in which an effort must be made to prevent from going back to the old process. To do this, there should be documentation and an implementation of a monitoring plan. This should be institutionalized through training, incentives, staffing changes or upgrades.
Lean Method
The lead method or lean speed is a set of techniques and tools used to reduce waste that might arise in a given business process. It aims to identify and eliminate any steps that have no value-added or are deemed non-essential. The result is a streamlined production/operational process, enhanced quality control, and improved customer loyalty.
Lean Six Sigma (LSS) Method
The LSS Method is made up of concepts derived from Six Sigma and the Lean Method. The combined management approach amplifies the strengths of both approaches while lessening their weaknesses when used separately. Essentially, Six Sigma focuses on improving quality while the Lean Method focuses on removing or eliminating waste.
Certification Methods
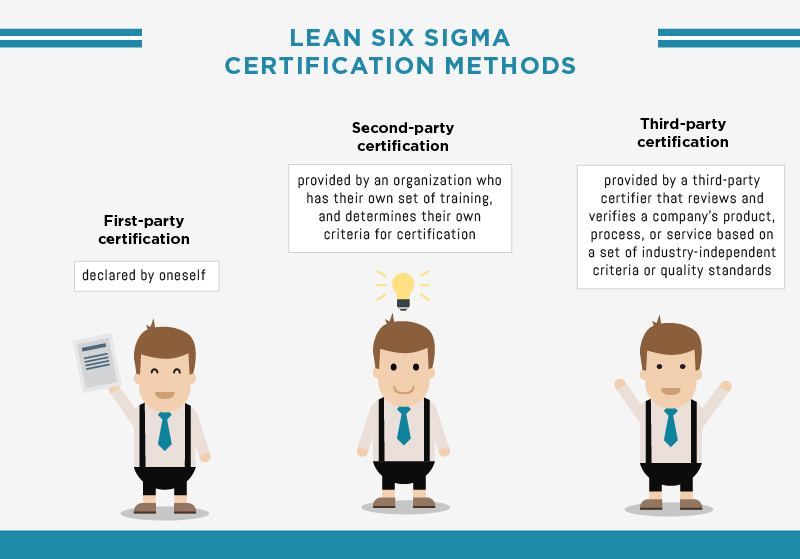
Certification methods are classified as first-party, second-party, and third-party.
The first-party certification is simply self-declaration.
Second-party certification is provided by an organization who has their own set of training and determines their own criteria for certification.
Third-party certification is one in which an impartial third-party certifier reviews and verifies that a company’s product, process, or service requirements are met based on a set of industry-independent criteria or quality standards.
Who Provides LSS Belt Certification?
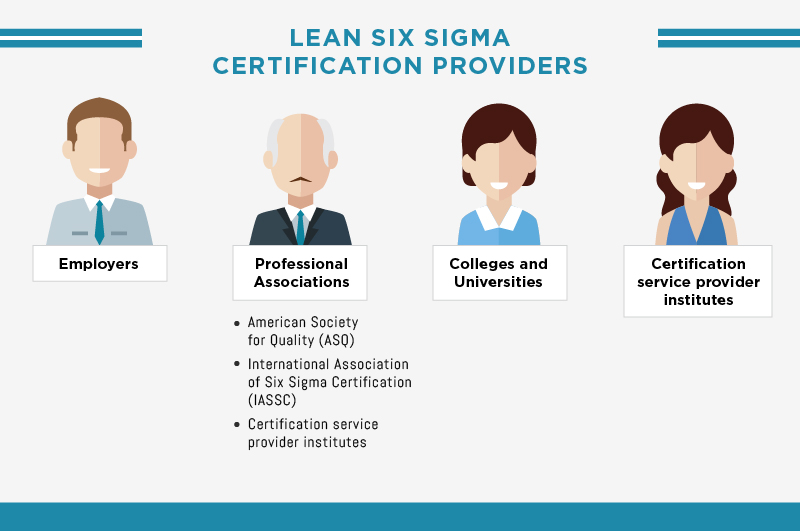
The four main providers of Six Sigma Belt certification are the following:
Employers
This is where a company provides their training and grants second party certification to their employees. The company also pays for your training and determines a set of standards to encourage job success.
Professional Associations
Two of the most prominent LSS certifiers are the American Society for Quality (ASQ) and the International Association of Six Sigma Certification (IASSC)
ASQ – this third party certifier requires you to submit an application package that qualifies you to take the exam, which typically includes work history and project requirements; no course work is required.
IASSC – requires you to pass the LSS exam, and no project requirement. It can certify both individuals, as well as training programs.
Colleges and Universities
LSS training can be part of a school’s extended education or certification program, and does not require entrance exams or a degree from the university or college. Some offer self-paced, online course.
Certification service provider institutes
These certification bodies are typically run by Six Sigma gurus and high-level consultants who are well versed in its concepts and practical applications. A package of coursework, exam, project mentoring, guidance and other learning materials are usually provided.
Training can be provided to groups or individuals, where classes rotate across various locations, and intensive training is provided over a period. Self-paced and online learning sessions are typically limited within 365 days to complete the course.
Certified Lean Six Sigma Belts
A “belt” is provided to practitioners based on their level of experience. The darker the color, the more experience, training, skills, and knowledge it signifies.
This hierarchical structure is similar to martial arts. However, it differs in that you can obtain a black belt first without having to start from a lower level.
Black Belt
The lean six sigma black belt certification indicates expert knowledge and skills in Lean Methods, team leadership, and the DMAIC framework. You are expected to capably lead any team in executing LSS projects, as well as conduct training and serve as a coach or mentor to others.
Duration: typically 140-160 hours training or around four weeks, including instruction on statistical data analysis, leadership, project management, and designed experiments.
Green Belt
Green Belt is considered the intermediate level where members are considered essential participants of the LSS project team. Those with this belt have a strong knowledge and skill set related to DMAIC and Lean Methods, but not as much experience with advanced statistic tools such as Design of Experiments.
Duration: about less than 100 hours or about two weeks. Training includes instruction on basic statistics data analysis and a focus on team problem-solving techniques. Homework assignments timed online exams, and a presentation of a real-life project are typically required.
Yellow Belt
This is considered to be an advanced beginner level, as you are a knowledgeable contributor to LSS project and management, with familiarity about basic tools for improvement.
Yellow belt holders are quite versed in the basics of LSS concepts and project the support improvement as part of a team or conduct small projects once in a while.
Duration: At least 40 hours of training and a comprehensive timed exam are the requirements. There is no project requirement for Yellow Belts.
White Belt
This is the beginner level, where there is already an understanding of the overall application of process improvement. White belters have a working knowledge of the language of LSS.
Duration: About 4 hours of training, with no final exam or project requirements.
Obtaining a Lean Six Sigma designation provides you knowledge and skills needed to gain an edge in today’s competitive job market. Many employers often require job candidates to have at least a working understanding of its concepts. Even those who are already employed can stand to benefit from acquiring the certification since most companies require it if you want to be promoted within your organization.


